
Welcome to the dynamic world of futures trading, where financial markets come alive with opportunities for both hedgers and speculators. In this introduction guide, we’ll delve into the exciting realm of futures trading, with a specific focus on mini futures contracts. These smaller-sized contracts offer a gateway for individual investors to participate in the market’s movements without the hefty financial commitment required by standard contracts.
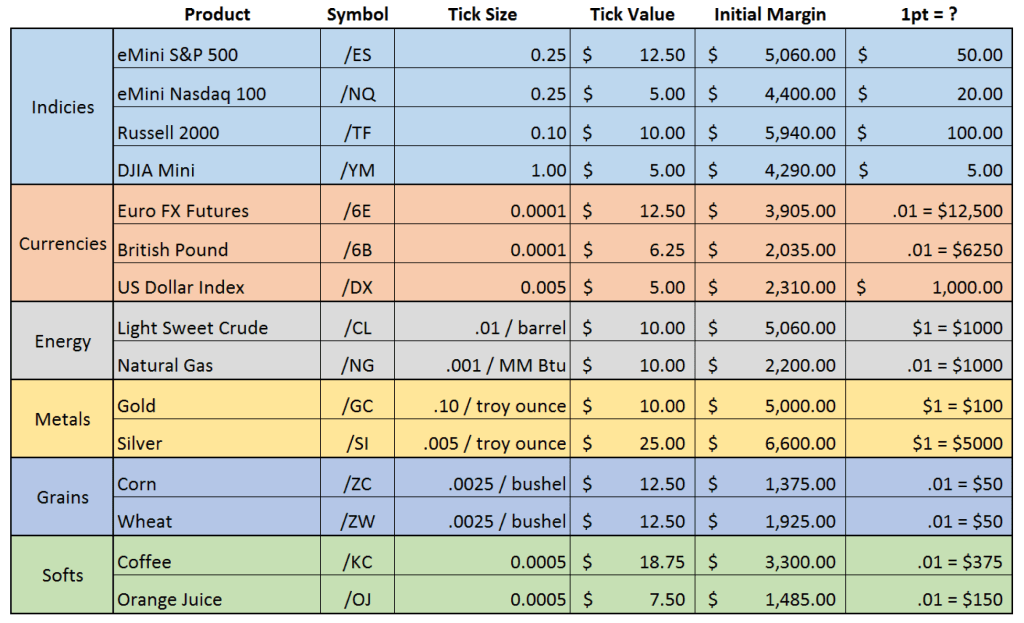
Advantages of Mini Futures Trading:
Conclusion:
Futures trading can be a powerful tool for managing risk and achieving financial goals. However, it comes with inherent risks, and beginners should approach it with caution. Continuous education, risk management, and a disciplined approach are key to success in the dynamic world of futures trading. Always start small, gain experience, and gradually increase your exposure as you become more confident in your trading abilities.